
Good afternoon,
Welcome to the best way to stay up-to-date on India’s financial markets. Here’s what is in today’s newsletter:
India plans to boost rare earth magnet production,
Apple expands partnership with Tata,
and Walmart-owned Flipkart secures RBI approval for direct landing.
Then, we close with Gupshup, a round-up of the most important headlines.
Have a question you want us to answer? Fill out this form and you could be featured in our newsletter.
—Shreyas, [email protected]
Market Update.
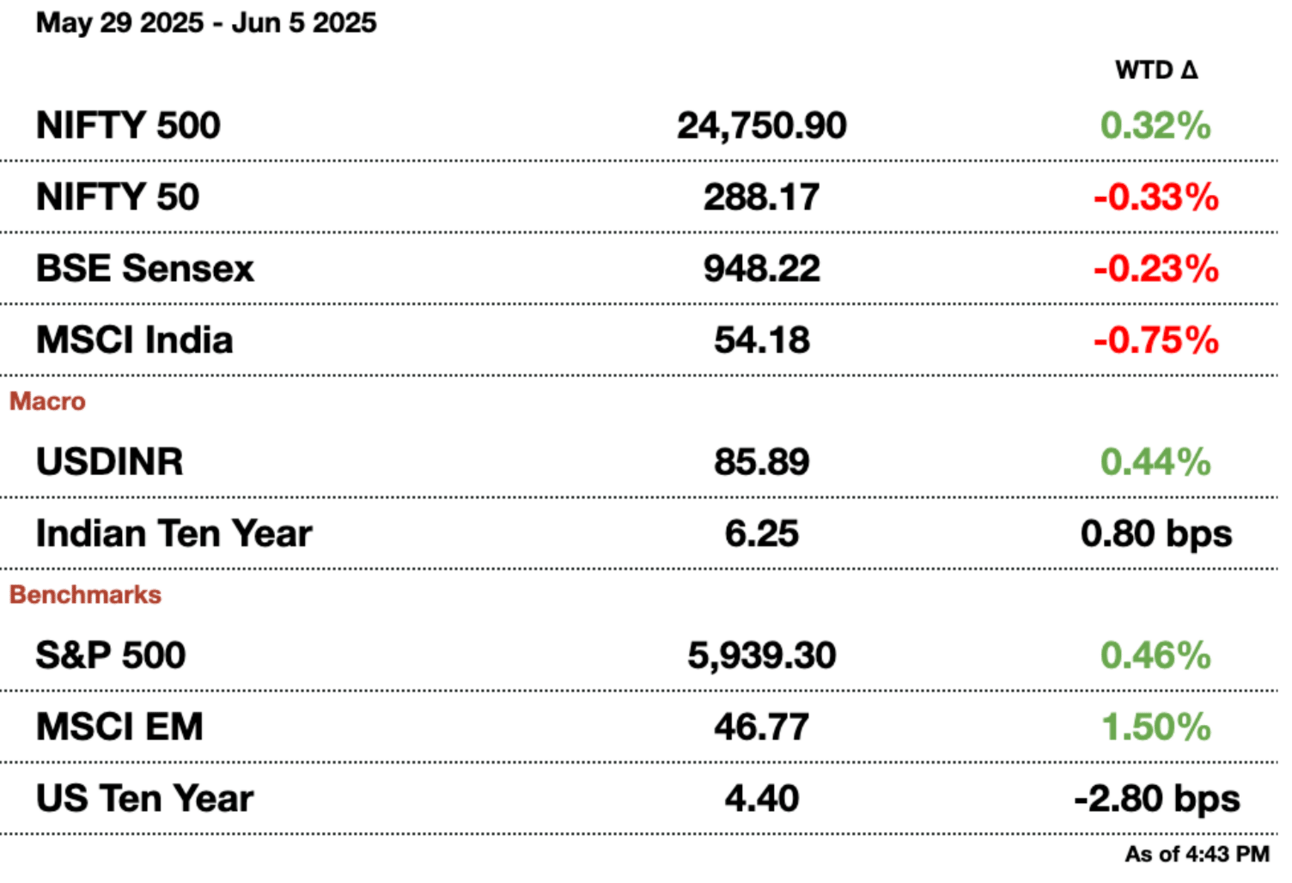
India Plans Incentives to Boost Rare Earth Magnet Production Amid Supply Concerns.
India is stepping up efforts to reduce its heavy dependence on China for rare earth magnets by considering fiscal incentives to encourage domestic production, according to sources familiar with the discussions.

Rare earth mineral ore
The move comes amid growing global supply chain disruptions triggered by China’s recent export restrictions on rare earth materials, a vital component for industries ranging from electric vehicles and clean energy to defense and electronics.
China currently dominates around 90 percent of the world’s processing capacity for rare earth magnets. India’s government, led by Prime Minister Narendra Modi, is now exploring ways to establish a local supply chain that could take years to fully develop but would significantly enhance the country’s industrial autonomy.
Incentivizing domestic production: Officials from India’s Ministry of Heavy Industries are drafting a scheme that would offer production-based fiscal incentives to manufacturers. The plan may also include subsidizing the cost gap between domestically produced magnets and cheaper Chinese imports, aiming to achieve cost parity and stimulate local demand, said two sources who requested anonymity due to the sensitivity of the talks.
Currently, India’s state-run firm IREL mines rare earth materials mainly for atomic energy and defense sectors, with most industrial demand still met through imports from China.
To address short-term supply risks, India plans to send a delegation of auto industry leaders to Beijing to seek expedited Chinese export approvals, although industry insiders acknowledge that a rapid supply chain shift is unlikely.
India’s untapped potential: India holds the world’s third-largest rare earth reserves, approximately 6.9 million tons, according to the U.S. Geological Survey. Yet, private sector investments in mining and processing remain limited, leaving much of the potential untapped.
The government’s National Critical Mineral Mission, launched in April, aims to foster self-reliance by boosting exploration and processing capabilities, particularly for neodymium, a key rare earth element used in magnets for electric and hybrid vehicles.
Prime Minister Modi’s office recently discussed the magnet supply challenges’ impact on India’s rapidly growing electric vehicle sector, which has attracted billions in investment. Officials are also considering tariff exemptions on machinery imports needed by domestic magnet manufacturers.
Apple Expands India Partnership With Tata for iPhone and MacBook Repairs.
Apple has expanded its partnership with Tata Group by assigning it responsibility for after-sales repairs of iPhones and MacBooks in India, according to two sources familiar with the matter. The move underscores Tata’s growing role in Apple’s global supply and service operations as the U.S. tech giant continues to shift its production footprint beyond China.

Tata has already emerged as a key Apple supplier, assembling iPhones at three manufacturing facilities in southern India for both domestic sales and exports. One of these facilities also produces select iPhone components. Now, the conglomerate is set to take over repair operations from ICT Service Management Solutions, an Indian subsidiary of Taiwan-based Wistron, marking another step forward in its strategic alignment with Apple.
The transition will see Tata handling complex repair work at its Karnataka facility, where iPhones are already assembled. Apple’s official service centers across India will continue to handle basic repairs and diagnostics, but devices requiring more advanced fixes will now be routed to Tata’s plant.
Why did Apple make this move? India is becoming an increasingly critical market for Apple, not only as a manufacturing hub but also as a growing consumer base. According to Counterpoint Research, iPhone sales in India reached approximately 11 million units in 2024, up from just 1 percent market share in 2020 to about 7 percent last year. The rising ownership of Apple devices is expected to drive demand for post-sales services, including repairs and refurbishments.
“Tata's deepening partnership with Apple could also pave the groundwork for Apple directly selling refurbished devices in India, like how it does in the United States currently,” said Prabhu Ram, Vice President at Cybermedia Research.
The change in service provider is already underway, though Apple and Wistron have not commented publicly. A Tata spokesperson also declined to comment. However, one source noted that Wistron’s ICT unit will continue servicing other clients, with Apple now being handled exclusively by Tata.
Longterm impacts: The broader partnership between Apple and Tata is part of a wider strategy to reduce reliance on Chinese production amid ongoing geopolitical uncertainties and potential U.S. tariffs. Apple CEO Tim Cook recently stated that the majority of iPhones sold in the U.S. during the June quarter will be manufactured in India, reflecting the company’s accelerating pivot toward South Asia.
With this latest development, Tata is not only solidifying its presence in Apple’s manufacturing network but also emerging as a central player in the after-sales ecosystem, positioning itself to benefit from Apple’s expanding footprint in India for years to come.
Walmart’s Flipkart Secures RBI Approval For Direct Lending in India.
Walmart-owned Flipkart has received regulatory approval to offer loans directly to customers and sellers in India, marking a major shift in how e-commerce platforms operate in the country’s growing digital credit space. A spokesperson for the company confirmed the development following a Reuters report that cited official documents and a source familiar with the matter.

In a first for India’s e-commerce sector, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has granted Flipkart a non-banking finance company (NBFC) licence. This designation allows the company to lend funds but not accept public deposits, opening the door to a potentially more profitable direct-lending model compared to the traditional partnerships with third-party lenders.
What this means for Flipkart: Until now, most Indian e-commerce platforms have relied on collaborations with banks or NBFCs to offer credit. With this licence, Flipkart becomes the first major e-commerce player in India to be officially recognized as a direct lender. This could help the company better manage customer experience, offer competitive rates, and gain greater control over its fintech operations.
Flipkart Finance Private Limited received its certificate of registration and formal approval from the RBI on March 13, according to documents reviewed by Reuters. The milestone had not been publicly disclosed until now.
The e-commerce giant, 80 percent owned by U.S. retail titan Walmart, first applied for the licence in 2022. According to a source close to the matter, Flipkart plans to launch its lending operations within the next few months. However, this timeline remains contingent on the completion of internal requirements, including the appointment of key management personnel and finalization of its lending framework.
The company aims to extend credit services via both its main e-commerce platform and its fintech app, ‘super.money.’ Loans will be offered not only to customers but also to sellers operating on the Flipkart marketplace, the source added.
Currently, Flipkart offers personal loans to users through partnerships with Axis Bank, IDFC Bank, and Credit Saison. Direct lending will allow it to eliminate intermediaries and enhance its margins.
Meanwhile, rival Amazon is following a similar path, having recently acquired Bengaluru-based NBFC Axio. However, that deal is still awaiting regulatory clearance from the RBI.
Message from our sponsor.
Learn AI in 5 minutes a day
This is the easiest way for a busy person wanting to learn AI in as little time as possible:
Sign up for The Rundown AI newsletter
They send you 5-minute email updates on the latest AI news and how to use it
You learn how to become 2x more productive by leveraging AI
Reach out to [email protected] to sponsor the next newsletter!
Gupshup.
Macro
The Reserve Bank of India is expected to cut interest rates by 25 basis points to 5.75 percent for the third consecutive time to support economic growth amid easing inflation and global challenges. Analysts will closely watch for dovish guidance on the pace of future cuts and updates on inflation, growth forecasts, and liquidity measures.
India’s benchmark indexes rose Thursday, led by Reliance Industries and rate-sensitive sectors like financials and real estate, ahead of an expected central bank rate cut. The Nifty 50 gained 0.53 percent to 24,750.90, and the Sensex rose 0.55 percent to 81,442.04. Reliance Industries climbed 1.3 percent after JPMorgan raised its target price, citing strong earnings prospects.
Equities
Ola Electric CEO Bhavish Aggarwal injected (₹2.33 million) ₹200 million in cash to maintain collateral for a loan backed by company shares, after a steep drop in Ola’s stock price amid declining market share and rising losses. The move aimed to support his AI startup Krutrim without triggering margin calls, even as Ola Electric faces governance concerns and investor exits.
Suzuki Motor has halted production of its flagship Swift subcompact car, excluding the Swift Sport version, since May 26 due to component shortages caused by China’s rare earth export restrictions. This makes Suzuki the first Japanese automaker impacted by these Chinese curbs, according to sources familiar with the situation.
Alts
Bargain hunters are eyeing India’s road sector as contract awards stay weak and stocks fall 23-48 percent from highs. Strong monsoon rains may boost agri-linked earnings, while rising border tensions could drive up defense spending and benefit industrial stocks.
France’s Dassault Aviation and India’s Tata Advanced Systems will manufacture the Rafale fighter jet fuselage in Hyderabad, marking the first time it will be produced outside France. India, the world’s largest arms importer, aims to increase domestic production and boost defense exports, which rose 12 percent to $2.76 billion (₹236.9 billion) in the fiscal year ending March.
Policy
Pakistan's Bilawal Bhutto Zardari warned that India’s use of a nuclear-capable missile in a recent conflict has dangerously lowered the threshold for war, increasing the risk of rapid escalation. He called for urgent dialogue to prevent future clashes between the two nuclear-armed neighbors.
Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi was not invited to the upcoming Canada-hosted G-7 summit, marking a diplomatic setback and reflecting strained India-Canada relations over allegations of Indian involvement in crimes targeting Sikh separatists in Canada. Even if invited, Modi was unlikely to attend amid unresolved concerns about Sikh groups in Canada, underscoring the ongoing diplomatic rift.
See you Friday.
Written by Yash Tibrewal. Edited by Shreyas Sinha.
Disclaimer: This is not financial advice or recommendation for any investment. The Content is for informational purposes only, you should not construe any such information or other material as legal, tax, investment, financial, or other advice.

